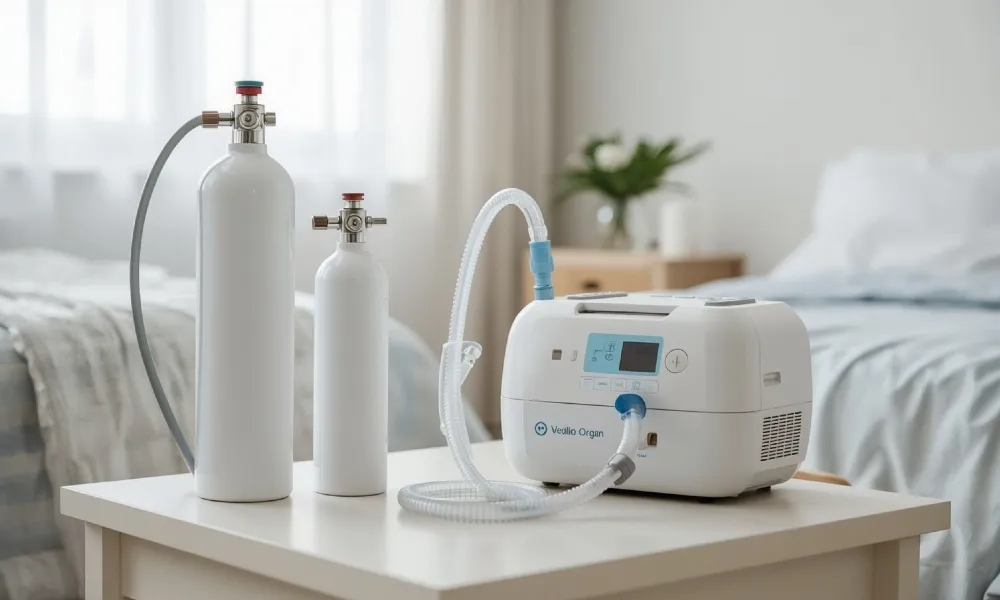
An oxygen concentrator is a medical device designed to provide supplemental oxygen to people who have difficulty breathing or low blood oxygen levels. Unlike oxygen cylinders, which store a limited amount of compressed oxygen, an oxygen concentrator continuously produces oxygen from the surrounding air. This makes it a reliable, cost-effective, and convenient solution for long-term oxygen therapy at home, in hospitals, and during travel.
What Is an Oxygen Concentrator?
An oxygen concentrator is an electrically powered device that extracts oxygen from ambient air and delivers it to the patient in a concentrated form. Normal air is made up of about 21% oxygen, nearly 78% nitrogen, with trace amounts of other gases. An oxygen concentrator increases the oxygen concentration to about 90-95%, which is suitable for most medical needs.
It is often recommended for patients suffering from conditions such as:
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- Asthma
- Pneumonia
- Pulmonary fibrosis
- Post-COVID respiratory issues
- Heart failure and other lung-related disorders
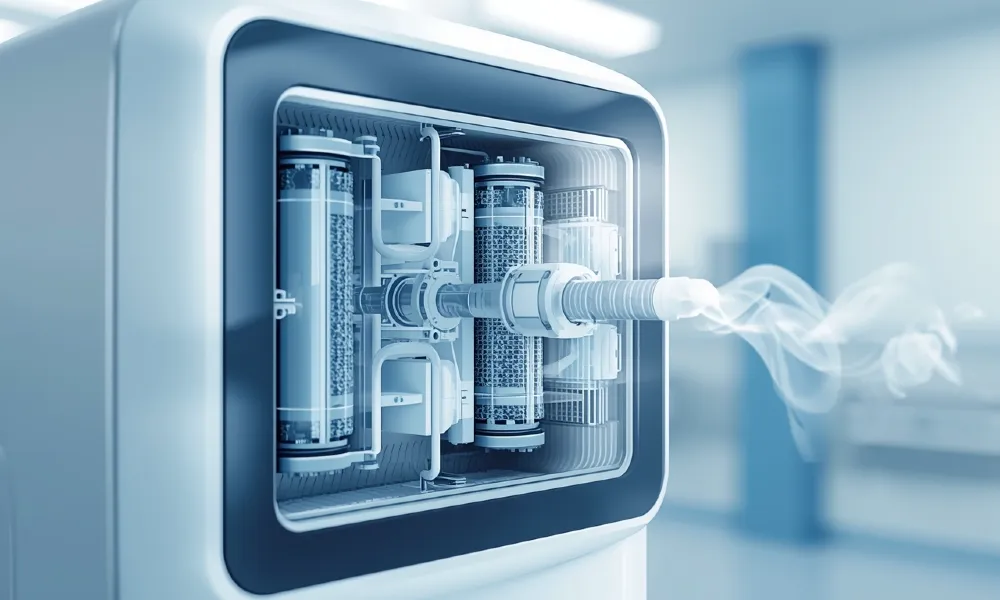
Main Components of an Oxygen Concentrator
To understand how an oxygen concentrator works, it’s important to know its key components:
- Air Intake Filter: Draws in room air and removes dust, bacteria, and impurities.
- Compressor: Pressurizes the filtered air to prepare it for oxygen separation.
- Sieve Beds (Zeolite Filters): Separate nitrogen from oxygen.
- Reservoir Tank: Stores concentrated oxygen temporarily.
- Flow Meter: Controls the rate of oxygen delivery (liters per minute).
- Humidifier Bottle (Optional): Adds moisture to prevent dryness.
- Nasal Cannula or Mask: Supplies oxygen directly to the patient.
Step-by-Step: How an Oxygen Concentrator Works
- Air Intake: The concentrator pulls in air from the surrounding environment using a fan. This air first passes through external and internal filters that remove dust, pollutants, and microorganisms.
- Air Compression: The filtered air is then compressed by the internal compressor. Compressing the air is essential because it allows the device to efficiently separate oxygen from other gases.
- Nitrogen Separation Using Sieve Beds: This is the most critical step. The compressed air enters sieve beds filled with zeolite, a special material that selectively absorbs nitrogen. Oxygen passes through while nitrogen is trapped.
Most concentrators use two sieve beds that work alternately:
- One sieve bed absorbs nitrogen
- The other releases the trapped nitrogen back into the air
This continuous switching ensures a steady supply of concentrated oxygen.
- Oxygen Collection: After nitrogen is removed, the remaining oxygen-rich air (90–95% oxygen) is collected in a reservoir tank. This ensures smooth and uninterrupted oxygen flow to the patient.
- Oxygen Delivery: The oxygen is delivered through a flow meter that allows doctors or caregivers to set the prescribed oxygen flow rate. From there, oxygen travels through tubing to a nasal cannula or oxygen mask worn by the patient.
- Optional Humidification: For patients using oxygen for extended periods, dry oxygen can irritate the nasal passages. A humidifier bottle can be attached to add moisture, making breathing more comfortable.
Types of Oxygen Concentrators
1. Stationary Oxygen Concentrator
- Designed for home or hospital use
- Higher oxygen output (up to 10 LPM)
- Requires a continuous power supply
- Ideal for long-term therapy
2. Portable Oxygen Concentrator (POC)
- Lightweight and travel-friendly
- Battery-operated
- Lower oxygen output
- Suitable for active users and travel
Oxygen Concentrator vs Oxygen Cylinder
| Feature | Oxygen Concentrator | Oxygen Cylinder |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen Source | Produces oxygen from air | Stores compressed oxygen |
| Refilling | Not required | Requires refilling |
| Cost | Lower long-term cost | Higher recurring cost |
| Safety | Safer, no high pressure | High-pressure risk |
| Availability | Continuous | Limited supply |
What are the Benefits of Using an Oxygen Concentrator?
An oxygen concentrator is a reliable medical device that helps individuals with low oxygen levels breathe more comfortably and safely. It is widely used for home care, hospitals, and long-term oxygen therapy due to its efficiency and ease of use.
- Continuous Oxygen Supply: Produces oxygen directly from room air, ensuring uninterrupted support without refilling.
- Cost-Effective: Eliminates recurring cylinder refill costs, making it ideal for long-term use.
- Safe to Use: No high-pressure oxygen storage, reducing the risk of leaks or accidents.
- Easy Operation: Simple controls allow patients and caregivers to use it without technical expertise.
- Portable Options Available: Portable oxygen concentrators support mobility and travel.
- Improves Quality of Life: Helps reduce breathlessness, fatigue, and supports faster recovery.
- Low Maintenance: Requires basic cleaning of filters and minimal upkeep.
- Environment Friendly: Reduces dependence on disposable oxygen cylinders.
Overall, an oxygen concentrator offers a dependable, safe, and convenient solution for oxygen therapy, making it an excellent choice for patients who need consistent respiratory support at home or on the go.
Safety Tips While Using an Oxygen Concentrator
- Keep the device in a well-ventilated area
- Clean filters regularly
- Avoid smoking or open flames nearby
- Use the prescribed flow rate only
- Ensure proper power backup during an outage
Who Needs an Oxygen Concentrator?
An oxygen concentrator is recommended when blood oxygen saturation falls below normal levels. A doctor determines the requirement based on tests like pulse oximetry or arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis.
It can be used for:
- Short-term recovery
- Long-term chronic conditions
- Home care and elderly patients
Wrapping Up
An oxygen concentrator works by drawing in ambient air, filtering out nitrogen, and delivering high-purity oxygen to patients who need respiratory support. Its ability to provide a continuous, reliable oxygen supply without refilling makes it an essential medical device for home and clinical use. Understanding how an oxygen concentrator works helps patients and caregivers use it safely, effectively, and with confidence.
If you or a loved one requires oxygen therapy, consult a healthcare professional to choose the right type and flow rate for your needs.
Don’t Miss: What is the 3% Rule for Sleep Apnea?